Lipoma Treatment: You Can Try Now
- Bisma Jamal
- Sep 23, 2024
- 7 min read
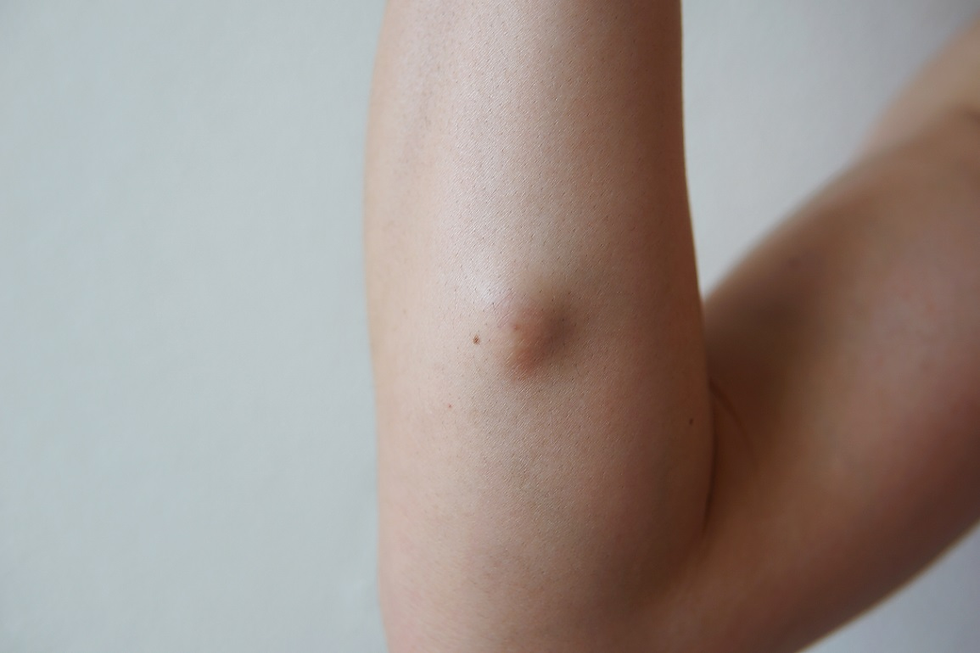
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor made up of fat tissue. It typically appears as a soft, movable lump under the skin and can occur anywhere on the body, though it’s most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, and thighs. Lipoma Treatments in Dubai are generally painless and slow-growing, often posing no serious health risks. However, some individuals seek treatment for cosmetic reasons, discomfort, or if the lipoma grows near a nerve or vital organ.
Lipoma Treatment: Why Consider It?
While lipomas are benign and usually harmless, there are several reasons why someone might consider treatment. These reasons include:
Cosmetic Concerns: A visible lipoma, especially on the face or neck, can affect a person's self-esteem and confidence.
Discomfort or Pain: If a lipoma grows large or is located near a nerve or joint, it can cause discomfort or pain.
Mobility Issues: In rare cases, a lipoma can grow large enough to restrict movement, particularly if it’s located near a joint.
Uncertainty: Sometimes, a lipoma can be mistaken for a more serious condition like liposarcoma, a malignant tumor. Treatment or removal may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Non-Surgical Lipoma Treatment Options
For those who prefer not to undergo surgery, several non-surgical treatments are available. These options are generally less invasive and may be suitable for smaller or less problematic lipomas.
1. Steroid Injections
Steroid injections are a common non-surgical treatment option for lipomas. A corticosteroid, often a type like triamcinolone, is injected directly into the lipoma. The steroid works by shrinking the lipoma, although it usually doesn’t completely eliminate it.
How It Works: The corticosteroid reduces inflammation and fat cell proliferation, leading to a reduction in the size of the lipoma.
Effectiveness: This method is generally more effective for smaller lipomas and may require multiple injections over time.
Pros: Minimally invasive, quick procedure with no downtime.
Cons: The lipoma may not completely disappear, and there’s a possibility it could grow back.
2. Liposuction
Liposuction, a procedure more commonly associated with cosmetic fat removal, can also be used to treat lipomas. This method involves using a suction technique to remove the fatty tissue from the lipoma.
How It Works: A small incision is made near the lipoma, and a thin, hollow tube called a cannula is inserted. The cannula is moved back and forth to loosen the fat, which is then suctioned out.
Effectiveness: Liposuction can effectively reduce the size of the lipoma, though it may not remove all of the fatty tissue, which can sometimes lead to recurrence.
Pros: Less invasive than surgical removal, minimal scarring.
Cons: There’s a risk of the lipoma returning if not all the fatty tissue is removed. Some residual fat may remain.
3. Injection Lipolysis
Injection lipolysis is another non-surgical method used to treat lipomas. This technique involves injecting a substance, often deoxycholic acid, into the lipoma to dissolve the fat cells.
How It Works: Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally produced by the body to absorb fat. When injected into the lipoma, it breaks down the fat cells, which the body then naturally absorbs.
Effectiveness: This treatment is typically more effective for smaller lipomas and may require multiple sessions.
Pros: Minimally invasive, no scarring, and suitable for those who prefer to avoid surgery.
Cons: Multiple treatments may be needed, and there’s a chance of recurrence if the lipoma isn’t completely dissolved.
4. Cryolipolysis (Fat Freezing)
Cryolipolysis, commonly known as CoolSculpting, is a procedure that uses controlled cooling to freeze and destroy fat cells. It’s typically used for cosmetic fat reduction but can also be applied to lipomas.
How It Works: The area containing the lipoma is exposed to very cold temperatures, which freeze the fat cells. Over time, the body naturally eliminates these dead cells.
Effectiveness: This method can effectively reduce the size of the lipoma, though it may not completely remove it.
Pros: Non-invasive, no needles or incisions, and minimal downtime.
Cons: Results are gradual, and multiple treatments may be needed. The lipoma may not be entirely removed, and there is a risk of recurrence.
Surgical Lipoma Treatment Options
Surgical removal is often considered the most definitive treatment for lipomas, especially for larger or more problematic lumps. While surgery involves some risks and recovery time, it is typically the most effective way to completely remove a lipoma.
1. Excision Surgery
Excision surgery is the most common and straightforward method for removing a lipoma. This procedure involves making an incision in the skin and surgically removing the entire lipoma.
How It Works: The surgeon makes an incision over the lipoma and carefully removes the fatty tissue, ensuring that all of it is extracted to prevent recurrence. The incision is then closed with sutures.
Effectiveness: Excision surgery is highly effective, with a low risk of the lipoma returning if the entire tumor is removed.
Pros: Complete removal of the lipoma, minimal chance of recurrence, and the ability to perform a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Cons: Involves an incision, which may result in scarring. There’s also a recovery period that may involve some discomfort and limited activity.
2. Minimal Excision Extraction
Minimal excision extraction is a variation of excision surgery that uses a smaller incision. This technique aims to minimize scarring while still effectively removing the lipoma.
How It Works: The surgeon makes a small incision, just large enough to extract the lipoma. The fatty tissue is removed through this small opening, and the incision is closed with sutures or adhesive strips.
Effectiveness: This method is effective for smaller lipomas and results in less scarring compared to traditional excision surgery.
Pros: Minimal scarring, effective removal, and quicker recovery time.
Cons: May not be suitable for larger lipomas, and there’s a slight risk of incomplete removal, leading to recurrence.
3. Endoscopic Removal
Endoscopic removal is a more advanced surgical technique that uses an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) to assist in the removal of the lipoma. This method is particularly useful for lipomas located in deeper tissues or in more sensitive areas.
How It Works: The surgeon makes a small incision and inserts the endoscope, which allows them to visualize the lipoma and surrounding tissues. The lipoma is then removed using specialized instruments.
Effectiveness: Endoscopic removal is highly effective for lipomas that are difficult to access or located near vital structures.
Pros: Minimally invasive, precise removal, and minimal scarring.
Cons: Requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it less widely available. The procedure may also take longer than traditional excision.
Emerging Lipoma Treatment Options
As medical technology advances, new treatments for lipomas are emerging that offer less invasive alternatives to traditional surgery. These treatments are still in the experimental or early adoption stages but show promise in providing effective results with fewer side effects.
1. Laser-Assisted Lipoma Removal
Laser-assisted lipoma removal is a relatively new technique that uses laser technology to precisely remove lipomas. The laser can help minimize bleeding, reduce scarring, and speed up the healing process.
How It Works: A laser is used to make a small incision in the skin and then carefully dissect the lipoma from surrounding tissues. The laser’s heat helps to seal blood vessels, reducing bleeding and promoting faster recovery.
Effectiveness: This method is effective for small to medium-sized lipomas and can result in less post-operative pain and scarring.
Pros: Minimally invasive, less bleeding, reduced scarring, and quicker recovery.
Cons: Not widely available, and may not be suitable for larger or more complex lipomas.
2. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction
Ultrasound-assisted liposuction is an advanced form of liposuction that uses ultrasound waves to liquefy the fat in the lipoma before removal. This technique can make it easier to extract the fatty tissue and may result in a more complete removal.
How It Works: Ultrasound energy is applied to the lipoma to break down the fat cells, which are then suctioned out using a cannula. The ultrasound also helps to minimize trauma to surrounding tissues.
Effectiveness: This method is effective for reducing the size of the lipoma and can result in a more thorough removal compared to traditional liposuction.
Pros: Minimally invasive, more complete fat removal, and reduced risk of recurrence.
Cons: Requires specialized equipment and training, and there’s a possibility of burns or other complications if not performed correctly.
Aftercare and Recovery
Regardless of the treatment method chosen, aftercare is an important aspect of the recovery process. Proper aftercare can help minimize complications, reduce scarring, and ensure the best possible outcome.
Wound Care: If an incision was made, keeping the wound clean and dry is crucial. Follow your doctor’s instructions on how to care for the wound, including when to change bandages and how to clean the area.
Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort is common after any lipoma treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication.
Activity Restrictions: Depending on the size and location of the lipoma, you may need to avoid certain activities for a period of time. This could include heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, or any activity that puts strain on the treated area.
Monitoring for Complications: It’s important to monitor the treated area for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, increased pain, or discharge. If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Follow-Up Appointments: Your doctor will likely schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and ensure that the lipoma has been fully removed. These appointments are also an opportunity to address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Conclusion
Lipomas are generally harmless, but they can cause discomfort, affect your appearance, or raise concerns about underlying health conditions. Fortunately, a variety of treatment options are available, ranging from non-surgical methods like steroid injections and liposuction to surgical options like excision and emerging techniques like laser-assisted removal. By understanding these options and working with a qualified healthcare provider, you can choose the treatment that best suits your needs and achieve the best possible outcome.



Comments